Mastering CI/CD Pipelines: A Comprehensive Guide to GitHub Actions on Linux
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Linux DevOps news, the convergence of development and operations has never been more critical. As organizations strive for faster deployment cycles and higher code quality, Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) have become the bedrock of modern software engineering. Among the myriad of tools available, GitHub Actions has emerged as a powerhouse, particularly when paired with the versatility of the Linux ecosystem. Whether you are tracking Ubuntu news for the latest LTS stability or following Arch Linux news for bleeding-edge developments, understanding how to leverage GitHub Actions on Linux infrastructure is essential for today’s developers and system administrators.
This article provides an in-depth technical exploration of orchestrating workflows using GitHub Actions. We will move beyond basic setups to explore complex scenarios involving Docker Linux news, container orchestration, and system-level automation. By integrating concepts from Linux automation news and Linux security news, we aim to build pipelines that are not only efficient but also secure and resilient. From configuring self-hosted runners on Debian news based servers to deploying microservices, this guide covers the spectrum of modern CI/CD practices.
Core Concepts: The Linux Runner Ecosystem
At the heart of GitHub Actions lies the “runner”—the compute instance that executes your workflow jobs. While GitHub provides hosted runners (typically based on Ubuntu), the true power for enterprise and specialized workloads often lies in understanding the underlying Linux architecture. When following Red Hat news or CentOS news, you realize that enterprise environments often require specific kernel modules or compliance standards that standard hosted runners might not provide.
Virtual Environments vs. Containerized Jobs
GitHub’s hosted Linux runners are virtual machines. However, for Alpine Linux news enthusiasts who prefer lightweight execution, Actions supports running jobs directly inside Docker containers. This allows you to test against specific distributions—be it Fedora news releases or openSUSE news updates—without changing the host infrastructure.
Below is a fundamental workflow configuration. This example demonstrates a matrix build strategy, a common pattern in Linux development news, ensuring software compatibility across different Python versions and operating system environments.
name: Cross-Platform Linux CI
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
jobs:
build-and-test:
name: Test on ${{ matrix.os }}
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [ubuntu-22.04, ubuntu-20.04]
python-version: ["3.10", "3.11"]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Install System Dependencies
run: |
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y libpq-dev gcc
# Relevant for Linux administration news regarding package management
- name: Install Python Dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
if [ -f requirements.txt ]; then pip install -r requirements.txt; fi
- name: Run Tests with Pytest
run: |
pip install pytest
pytest tests/ --verboseIn the example above, we utilize standard Linux commands news and package managers. The use of `sudo apt-get` highlights the integration with apt news and Linux package managers news. If you were running this on a Red Hat-based self-hosted runner, you would adapt this to use `dnf` or `yum`, reflecting the diversity found in Rocky Linux news and AlmaLinux news.
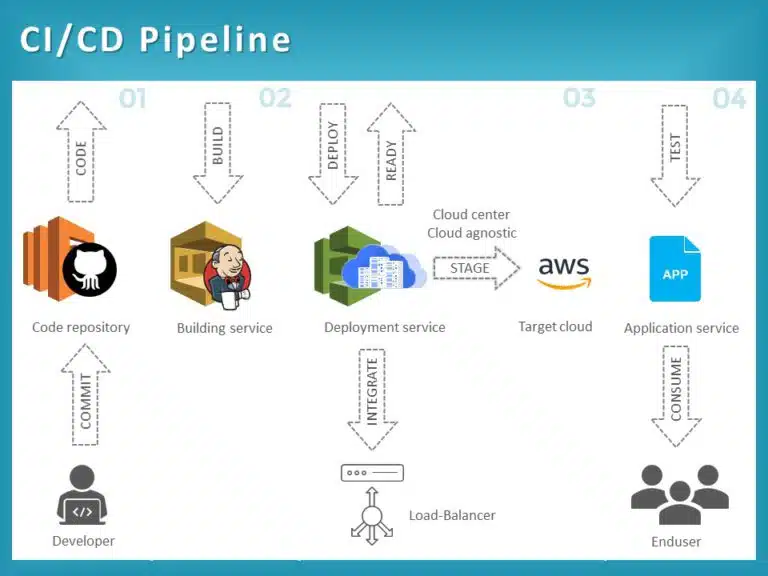
Implementation Details: Scripting and Automation
Open source code on screen – What Is Open-Source Software? (With Examples) | Indeed.com
Effective CI/CD on Linux often requires dropping down into shell scripting. Whether you are a fan of bash news, zsh news, or fish shell news, the ability to script complex logic is vital. This is particularly true when dealing with Linux file permissions news or preparing environments for Linux database news like PostgreSQL Linux news or MySQL Linux news.
Advanced Shell Integration
Let’s look at a scenario involving Linux server news and deployment preparation. Often, a workflow needs to verify system integrity, check for Linux security news patches, or configure Linux firewall news settings (like iptables news or nftables news) before a deployment occurs. While GitHub hosted runners are ephemeral, these scripts are crucial for self-hosted runners managing persistent infrastructure.
Here is a Python script designed to be executed within an Action to validate environment configurations and check for necessary Linux networking news tools before proceeding with a build.
import subprocess
import sys
import os
def check_command(command):
"""Verifies if a Linux command exists in the environment."""
try:
subprocess.check_output(["which", command])
return True
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
return False
def validate_environment():
print("Starting Environment Validation...")
# Critical tools for Linux DevOps news workflows
required_tools = ["docker", "git", "curl", "openssl"]
missing_tools = []
for tool in required_tools:
if check_command(tool):
print(f"[OK] {tool} is present.")
else:
print(f"[ERROR] {tool} is missing.")
missing_tools.append(tool)
# Check for specific environment variables (Security best practices)
if "DEPLOY_KEY" not in os.environ:
print("[WARNING] DEPLOY_KEY not found in environment variables.")
if missing_tools:
print(f"Build failed due to missing tools: {', '.join(missing_tools)}")
sys.exit(1)
print("Environment validation successful.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
validate_environment()This script can be integrated into your YAML workflow using a simple `run: python validate_env.py` step. It bridges the gap between high-level orchestration and low-level Linux administration news. It ensures that tools relevant to Linux containers news (like Docker) and Linux encryption news (like OpenSSL) are available.
Advanced Techniques: Container Orchestration and IaC
As we delve deeper into Kubernetes Linux news and Linux cloud news, the complexity of workflows increases. Modern pipelines often involve building container images, scanning them for vulnerabilities (a hot topic in Linux security news), and deploying them to clusters managed by OpenShift or standard Kubernetes.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Integration
Integrating Terraform Linux news or Ansible news into GitHub Actions allows for complete infrastructure lifecycle management. You can provision Linux web servers news (Nginx, Apache) or configure Linux load balancers news (HAProxy) dynamically. Below is an advanced workflow snippet that builds a Docker image, pushes it to a registry, and triggers a rollout, touching upon Linux virtualization news concepts.
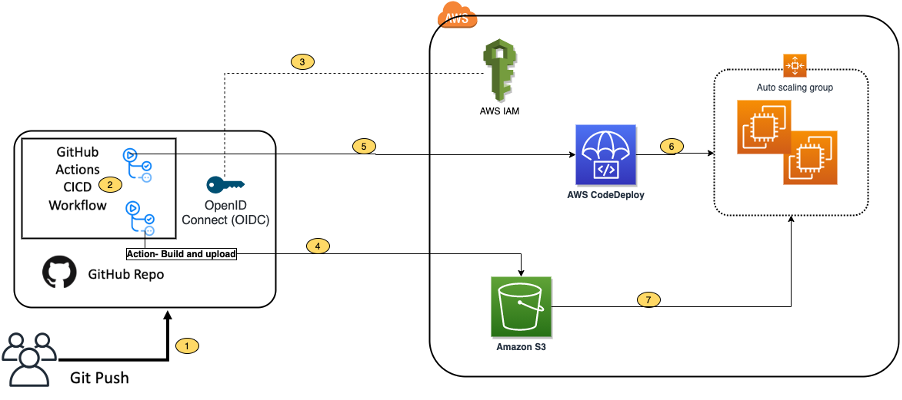
name: Docker Build and K8s Deploy
on:
release:
types: [published]
env:
REGISTRY: ghcr.io
IMAGE_NAME: ${{ github.repository }}
jobs:
build-and-push:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
packages: write
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Log in to the Container registry
uses: docker/login-action@v2
with:
registry: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
username: ${{ github.actor }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Extract metadata (tags, labels)
id: meta
uses: docker/metadata-action@v4
with:
images: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}
- name: Build and push Docker image
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
with:
context: .
push: true
tags: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
labels: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.labels }}
# Leveraging Linux caching mechanisms for speed
cache-from: type=gha
cache-to: type=gha,mode=max
deploy:
needs: build-and-push
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Install kubectl
uses: azure/setup-kubectl@v3
- name: Deploy to Cluster
env:
KUBE_CONFIG: ${{ secrets.KUBE_CONFIG }}
run: |
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
echo "$KUBE_CONFIG" > $HOME/.kube/config
chmod 600 $HOME/.kube/config
# Rolling update command relevant to Kubernetes Linux news
kubectl rollout restart deployment/my-app -n productionThis workflow exemplifies the synergy between Docker Linux news and CI/CD. It utilizes advanced caching (relevant to Linux performance news) to speed up builds. Furthermore, the deployment step interacts with Linux clustering news technologies, ensuring high availability.
Open source code on screen – Open-source tech for nonprofits | India Development Review
Best Practices and Optimization
To truly master GitHub Actions on Linux, one must look beyond the syntax and consider the operational context. This includes monitoring, security, and hardware optimization. Whether you are running on Linux laptop news hardware for local testing or massive server farms, the principles remain consistent.
Security and Permissions
With the rise of supply chain attacks, Linux security news is dominated by discussions on securing pipelines. Always use the principle of least privilege. In the YAML example above, notice the `permissions` block. This restricts what the GITHUB_TOKEN can do, a practice aligned with Linux SELinux news and AppArmor news philosophies of mandatory access control.
Self-Hosted Runners and Hardware
For those following Linux hardware news, you might be deploying actions on Raspberry Pi Linux news devices for IoT projects or high-performance servers for Linux gaming news compilation (like compiling shaders for Vulkan Linux news). Managing self-hosted runners requires robust Linux systemd timers news and Linux logs news management.
Open source code on screen – Design and development of an open-source framework for citizen …
Here is a shell script example for setting up a self-hosted runner service, ensuring it restarts automatically and logs correctly, leveraging systemd news.
#!/bin/bash
# Setup script for a self-hosted runner on a Debian/Ubuntu system
# Relevant for Linux administration news and automation
RUNNER_VERSION="2.303.0"
RUNNER_DIR="/opt/actions-runner"
USER="github-runner"
# Ensure script is run as root
if [ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]; then
echo "Please run as root"
exit
fi
# Create user if not exists (Linux user management)
if ! id "$USER" &>/dev/null; then
useradd -m $USER -s /bin/bash
fi
mkdir -p $RUNNER_DIR && cd $RUNNER_DIR
# Download runner (Simulating curl/wget usage common in Linux networking news)
curl -o actions-runner-linux-x64-${RUNNER_VERSION}.tar.gz -L https://github.com/actions/runner/releases/download/v${RUNNER_VERSION}/actions-runner-linux-x64-${RUNNER_VERSION}.tar.gz
tar xzf ./actions-runner-linux-x64-${RUNNER_VERSION}.tar.gz
# Fix permissions (Linux file permissions news)
chown -R $USER:$USER $RUNNER_DIR
# Install dependencies
./bin/installdependencies.sh
echo "Runner installed. Please configure using ./config.sh as the '$USER' user."
echo "Then install the systemd service using: sudo ./svc.sh install"This script touches on critical administrative tasks: user management, file permissions, and service installation. It ensures that your CI/CD infrastructure is as robust as the Linux kernel news updates that power it.
Conclusion
The integration of GitHub Actions with the Linux ecosystem represents a significant leap forward in Linux open source news. By combining the flexibility of Linux—from Manjaro news desktops to Enterprise Linux servers—with the automation capabilities of GitHub Actions, developers can build pipelines that are both powerful and agnostic to the underlying infrastructure.
We have explored core concepts involving runners and matrices, implemented Python and Shell-based automation, and dived into advanced Docker and Kubernetes deployments. As you continue to follow Linux DevOps news, remember that the landscape is always changing. Tools like Podman news may offer alternatives to Docker, and Wayland news might change how GUI tests are run. Staying adaptable and mastering the fundamentals of Linux scripting and configuration management will ensure your CI/CD pipelines remain resilient in the face of change. Whether you are optimizing for Linux performance news or tightening security based on Linux forensics news, the code and strategies outlined here provide a solid foundation for your automation journey.



